In the field of modern materials science and industrial applications, high-performance composite materials are increasingly becoming the core force driving technological innovation. Among them, tungsten resin stands out as a unique tungsten-based polymer composite material due to its high density, radiation protection properties, and environmentally friendly characteristics. From radiation shielding in the nuclear industry to counterweight design in outdoor fishing gear, and to precision components in medical equipment, tungsten resin plays a key role in multiple high-demand scenarios. For any ratio and shape of tungsten resin products, please contact CTIA Tungsten Intelligence Technology Co., Ltd.: sales@chinatungsten.com, 0592-5129595. For more data on tungsten resin, please visit our website: http://www.tungsten-alloy.com/chinese/pinewood-derby-tungsten-alloy-putty.html
I. Definition and Composition of Tungsten Resin
Tungsten resin (Tungsten Resin), also known as resin tungsten polymer or tungsten-filled resin, is a functional material composited from high-purity tungsten powder and a thermoset or thermoplastic resin matrix. Its core lies in fusing the metallic properties of tungsten (such as high density and high hardness) with the polymer advantages of resin (such as flexibility and ease of processing), forming a composite product with controllable density and environmentally friendly, non-toxic characteristics.
The main components of CTIA tungsten resin include tungsten powder, resin matrix, and a small amount of additives, with proportion design being the key to performance optimisation. Tungsten powder: the highest proportion, usually 60–90 wt%. The tungsten powder has fine particle size and high purity, providing high density and radiation attenuation capability. Resin matrix: 10–40 wt%, common types include epoxy resin, polyurethane, or polyethylene. These polymers impart flexibility and bonding properties to the material, ensuring uniform dispersion of tungsten powder and preventing settling. Additives: small amount (<5 wt%), such as coupling agents (silane type) to improve the interface bonding between tungsten powder and resin; stabilisers (such as antioxidants) to enhance ageing resistance; pigments or fillers to adjust appearance and density.


II. Performance of Tungsten Resin
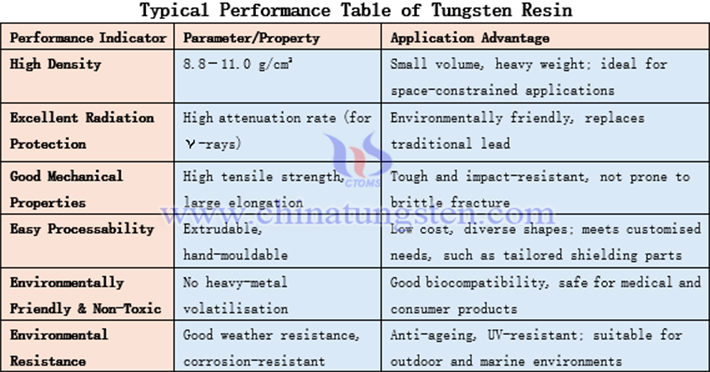
The performance of tungsten resin enables it to excel in high-precision and extreme environments. The excellent properties of tungsten resin stem from the uniform distribution of tungsten powder and the network structure of the resin.
III. Production Process of Tungsten Resin
Tungsten resin employs powder-filling composite technology, with a simple and efficient process. The production flow is as follows: First, in the raw material preparation stage, fine tungsten powder is mixed with resin prepolymer, and a coupling agent is added to modify the surface of the tungsten powder to improve its dispersibility in the resin. Subsequently, mixing and dispersion are carried out using a high-speed mixer or twin-screw extruder to ensure uniform incorporation of tungsten powder into the resin matrix, avoiding agglomeration, and vacuum degassing is used to remove bubbles and increase material density. In the moulding and curing stage, different processes are selected based on application needs: injection moulding is suitable for mass production, where the mixture is injected into a mould and then cured; hand moulding is suitable for small-batch production, such as tungsten putty that can be kneaded and cured at room temperature; extrusion moulding is used to produce rods or sheets, formed by continuous extrusion followed by cooling and cutting. Finally, post-processing such as surface polishing or coating is performed to enhance the aesthetics and wear resistance of the product.
During the production of tungsten resin, quality control is key to ensuring performance stability. X-ray scanning confirms no density stratification; γ-source testing verifies shielding rate compliance; universal testing machine validates tensile/impact properties; coordinate measuring machine locks in dimensions.
IV. Wide Application Fields of Tungsten Resin
(1) Radiation Shielding and Protection Field
A typical and mature use of tungsten resin is in radiation protection, replacing traditional lead materials; it is mouldable, non-toxic, non-metallic magnetic, friendly to the human body, and easy to form.
X-ray and γ-ray shielding: used in protective covers and collimators for medical equipment (X-ray machines, CT scanners); used in nuclear medicine injection protection containers and isotope transport boxes; used in laboratory shielding walls and γ-ray detector housings; used in maintenance protection modules for nuclear energy facilities.
Personal and mobile protection: lighter and more environmentally friendly than traditional lead protective cloth; used in wearable radiation protection gear, mobile detection shielding boxes, etc.
(2) Nuclear Energy and Radioisotope Science Applications
Nuclear fuel cladding or neutron absorption structures: adding tungsten powder to polyethylene or epoxy matrix enhances neutron and γ absorption; used in nuclear reactor experimental simulation materials and nuclear waste shielding containers.
Radioactive source calibration and shielding interlayer materials: high-density tungsten resin as a composite interlayer balances structural strength and protection performance.
(3) Aerospace and Military Applications
Inertial balance and counterweight materials: tungsten resin can be injection-moulded, with adjustable density and excellent damping properties; in satellites, spacecraft, and missile control systems, it is used for precision counterweights to control centre of gravity and moment of inertia.
Protective armour and penetration damping layers: used as energy-absorbing composite materials in explosion-proof vehicles and cabin partitions; layered with ceramics or carbon fibre to improve impact resistance and energy absorption.
(4) Electronics and Electromagnetic Applications
Electromagnetic wave shielding materials: due to its high-density characteristics, tungsten resin is suitable for aerospace electronics and medical imaging equipment; used in high-end electronic device housings, microwave absorption layers, and electromagnetic compatibility structural components.
Thermal management and heat-absorbing components: combining tungsten’s high thermal conductivity with resin’s insulation properties; used in thermal neutron absorbers, electric heater housings, high-temperature protective covers, and heat dissipation base plates.
(5) Precision Instruments and Industrial Fields
Non-magnetic high-density components: tungsten resin can be made into non-magnetic balance blocks, support bases, and vibration damping blocks; used in MRI equipment, precision machine tools, and gyroscope levelling devices.
Mould and tool filling materials: suitable for temperature control blocks and counterweights in injection moulds; improves mould life and thermal inertia.
(6) Medical Devices and Imaging Equipment
Injection-mouldable radiation-resistant structural parts: tungsten resin can replace metal parts to reduce weight and simplify assembly; used in X-ray collimators, CT machine support frames, and radiation window frames.
Radiation therapy auxiliary devices: used for cavity or implant protection, such as custom shielding parts to protect adjacent organs during tumour radiotherapy.
(7) 3D Printing and Advanced Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing removable mould materials: certain tungsten resins can be used for removable cores and heat-resistant filling structures.
(8) Art, Scientific Research, and Educational Uses
Tungsten resin can be used to create metal-like artworks (with a sense of weight); in experimental teaching to replace toxic heavy metals (such as lead blocks); as standard sample blocks for material density experiments.



