Note: This article provides a detailed introduction to tungsten hexafluoride (WF?), which has recently attracted significant attention, offering professional insights for readers. Experts are welcome to provide feedback, and interested readers are invited to join the discussion in the comments section.
Tungsten hexafluoride (chemical formula: WF?) is an inorganic compound and an important high-valence fluoride of tungsten. At standard temperature and pressure, it exists as a colorless, highly corrosive, and extremely toxic gas. Electronic-grade WF? typically requires purity of 6N (99.9999%) or higher, achieved through direct reaction of high-purity tungsten metal with fluorine gas followed by multi-stage purification processes.
WF? plays a critical role in industries such as electronics, chemicals, and manufacturing, particularly in semiconductor fabrication. It serves as a key precursor in chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes, decomposing at high temperatures to deposit tungsten thin films on wafer surfaces. These films are widely used in the formation of interconnects, gate electrodes, and barrier layers. Additionally, WF? finds important applications in display panel manufacturing and optical fiber communications.

Industry News: SK Specialty Announces WF? Price Increase
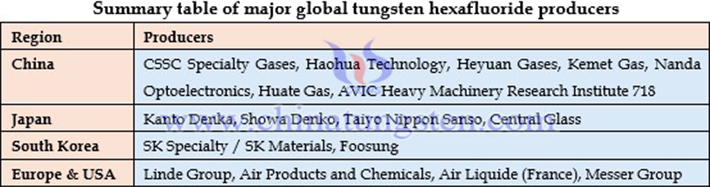
According to multiple media reports (late October 2025), several Japanese and Korean WF? suppliers, including SK Specialty, have notified major semiconductor manufacturers such as Samsung and SK Hynix of plans to raise WF? prices by 70%–90% starting in 2026. The price hike is primarily driven by rising tungsten raw material costs and tight global capacity for high-purity specialty gases, with suppliers citing the need to pass on increased production costs. Other affected fabs reportedly include DB HiTek and Magnachip.
The industry is currently assessing the impact of this price surge on wafer processing costs and long-term supply agreements. If implemented, the increase may lead to cost pass-through effects in existing orders and final device pricing. This development represents a significant variable in recent semiconductor supply chain cost volatility and warrants close attention to how Japan and South Korea leverage their dominance in tungsten-based products to influence China’s high-tech industries.
It is worth noting that China conducted successful WF? experiments as early as around 2010, but industrial-scale production was never realized. Currently, only a few domestic companies, including CSSC Specialty Gases and Haohua Chemical, possess electronic-grade WF? production technology. CSSC Specialty Gases, with an annual capacity of 2,000 tons, remains the leading domestic producer. This gap highlights a critical weakness in China’s high-end tungsten product manufacturing, prompting serious reflection within the industry.
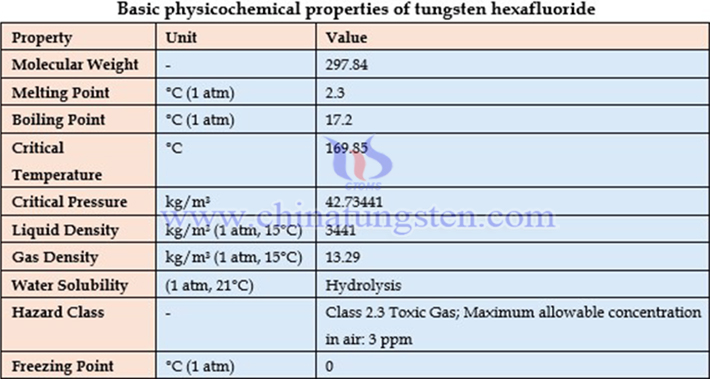
I. Basic Information on Tungsten Hexafluoride

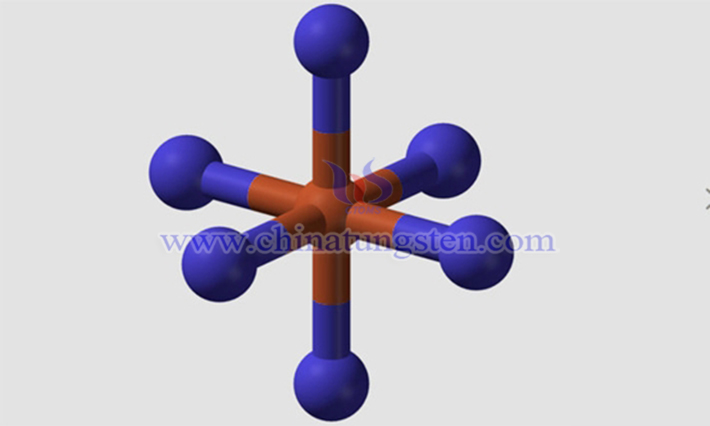
II. Structure and Chemical Properties of Tungsten Hexafluoride
1. Molecular Structure of Tungsten Hexafluoride
Tungsten hexafluoride adopts an octahedral geometry with Oh symmetry. The central tungsten atom is in the +6 oxidation state, surrounded by six equidistant fluorine atoms. All bond angles in the WF? molecule are 90°. The W–F bonds exhibit a mixture of strong polar and covalent character, with high bond energy and excellent chemical stability.
2. Physical Properties of Tungsten Hexafluoride
Tungsten hexafluoride is a gas at room temperature and highly volatile. It is highly hygroscopic, reacting with atmospheric moisture to form hydrogen fluoride (HF) and oxyfluorotungsten compounds (e.g., WO?F?, WO?). WF? is soluble in various non-polar solvents (such as CCl?) but reacts violently with water.
3. Chemical Properties of Tungsten Hexafluoride
WF? is a strong oxidizing and fluorinating agent. Key chemical reactions include:
(1) Reaction with Water (Highly Exothermic):
WF? + 3H?O → WO? + 6HF
Produces tungsten trioxide (WO?) and hydrogen fluoride (HF).
(2) Reaction with Metals (at Elevated Temperatures):
3Mg + WF? → 3MgF? + W
A typical chemical vapor deposition (CVD) reaction used to deposit pure tungsten thin films.
(3) Reduction Reactions: WF? can be reduced by hydrogen, ammonia, silane (SiH?), or diborane (B?H?) to form metallic tungsten.
WF? + 3H? → W + 6HF
?
III. Preparation Methods of Tungsten Hexafluoride
The following two routes are commonly employed in industry for the preparation of tungsten hexafluoride:
1. Direct Reaction of Tungsten Metal with Fluorine Gas
W + 3F? → WF?
This reaction is conducted at 300–400°C and represents the most widely used industrial method. The process must be carried out in nickel, copper, or Monel alloy reactors to prevent equipment corrosion.
2. Reaction of Tungsten Trioxide with Hydrogen Fluoride
WO? + 6HF → WF? + 3H?O
This method requires a higher reaction temperature (approximately 600°C), and the reaction atmosphere must be strictly controlled to avoid the formation of oxygen-containing byproducts.

IV. Main Applications of Tungsten Hexafluoride
1. Semiconductor Manufacturing – The Most Important Application of WF?
In chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes, WF? serves as a precursor for tungsten thin films.
Reaction: WF? + 3H? → W + 6HF
The resulting tungsten film is used for integrated circuit (IC) metallization layers, contact holes, and via filling. Advantages: Fast deposition rate, dense film formation, and high electrical conductivity.
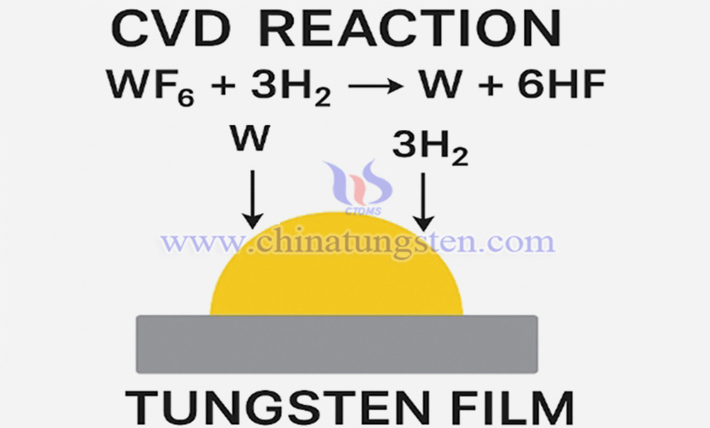
2. Surface Metallurgy and Protective Coatings
Tungsten hexafluoride can form a tungsten layer on metal surfaces via high-temperature decomposition or reduction, enhancing wear resistance and high-temperature durability.

3. Other Chemical Applications
Used as a fluorinating agent or intermediate in the synthesis of other tungsten fluorides and oxyfluorides. Serves as a precursor in advanced processes such as plasma chemistry and ion beam deposition.
V. Safety and Toxicity of Tungsten Hexafluoride
1. Hazardous Characteristics of WF?
WF? is a highly corrosive and toxic gas. It reacts with water or moist air to produce hydrogen fluoride (HF), which is intensely irritating and corrosive. Inhalation may cause respiratory tract burns, pulmonary edema, coughing, and asphyxiation. Contact with metal powders or combustible materials may trigger combustion or explosion.
2. Storage and Transportation of WF?
Must be stored in dry, sealed, corrosion-resistant high-pressure cylinders. During transportation, avoid shock, heat, and humid environments. Typically uses nickel or 316L stainless steel-lined containers.
3. Leakage Response for WF?
Evacuate personnel immediately and wear gas masks and chemical protective clothing. Neutralize the leaked area by spraying with alkaline solutions (e.g., NaOH or Ca(OH)?).
4. Environmental and Health Impacts of WF?
WF? does not persist long-term in the environment; it rapidly reacts with atmospheric moisture to form WO? and HF. Primary risks stem from its corrosivity and acute inhalation toxicity. It is not a greenhouse gas, but HF leakage during production or use can cause acidic pollution.
VI. Conclusion and Appendix
Conclusion
Tungsten hexafluoride (WF?) is critically important in high-tech industries, especially semiconductor manufacturing, and is an irreplaceable key material gas in the electronics sector. China holds an absolute resource advantage in the tungsten supply chain, yet significant gaps remain in high-end products such as high-purity tungsten compounds and high-performance alloys. This represents a key direction for innovation in China’s tungsten industry.
Appendix
? GB/T 32386-2015Gases for Electronic Industry — Tungsten Hexafluoride (Current National Standard)
? 20243664-T-469Electronic Gas — Tungsten Hexafluoride (National Standard Plan, Under Review)
? MSDS for Tungsten Hexafluoride (WF?) (Under Review)